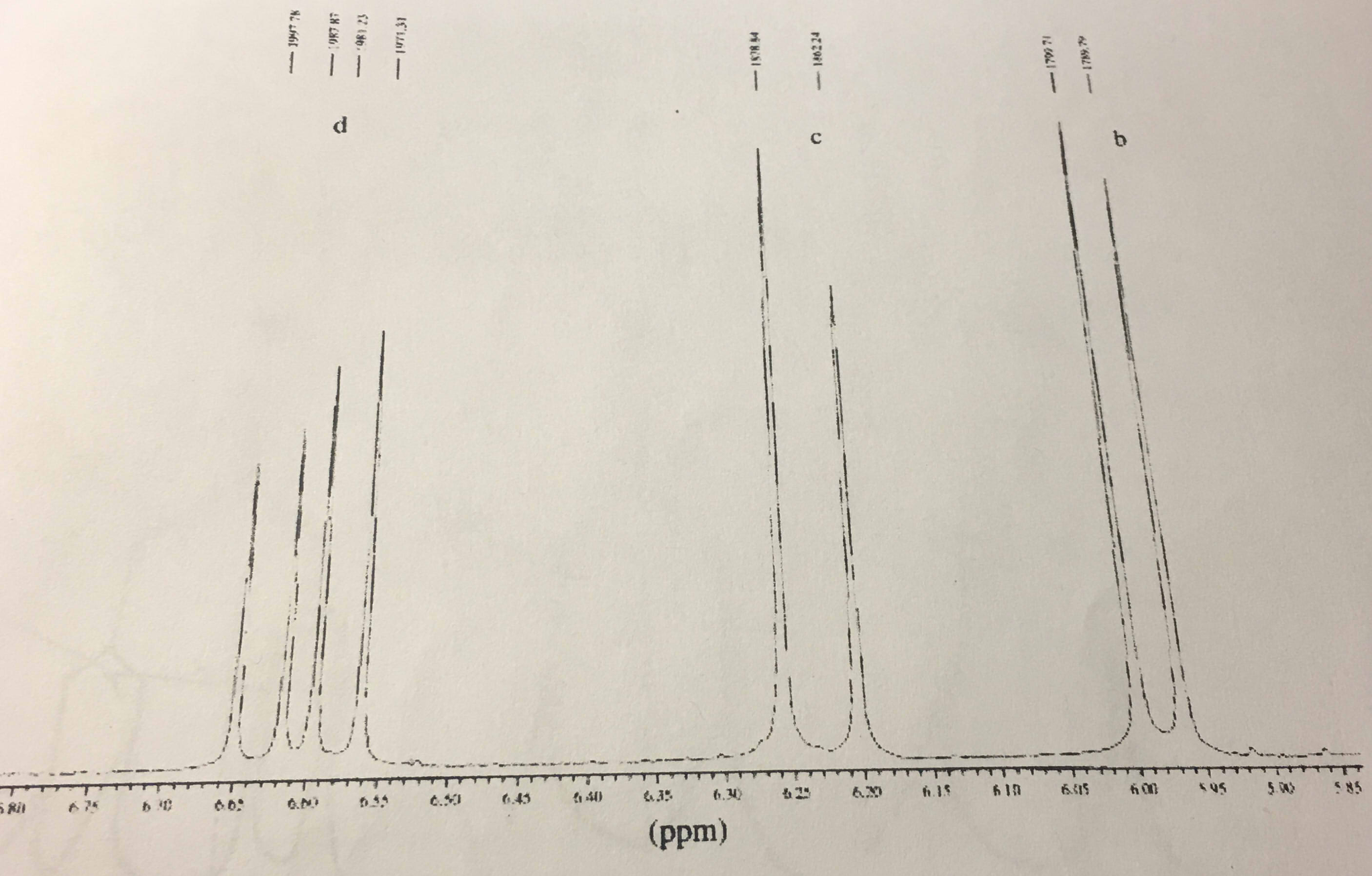
Vinylic r 2 c ch 2.
Vinylic proton nmr.
The induced field therefore augments the local field at the vinylic protons.
Proton nuclear magnetic resonance proton nmr hydrogen 1 nmr or 1 h nmr is the application of nuclear magnetic resonance in nmr spectroscopy with respect to hydrogen 1 nuclei within the molecules of a substance in order to determine the structure of its molecules.
Chemical shift is associated with the larmor frequency of a nuclear spin to its chemical environment.
0 8 1 5 ppm alkane c h.
Typical h nmr shift ranges.
The 1 h nmr spectra that we have seen so far of methyl acetate and para xylene are somewhat unusual in the sense that in both of these molecules each set of protons generates a single nmr signal in fact the 1 h nmr spectra of most organic molecules contain proton signals that are split into two or more sub peaks.
The 1 h nmr spectra that we have seen so far of methyl acetate and para xylene are somewhat unusual in the sense that in both of these molecules each set of protons generates a single nmr signal.
There are a lot of compounds especially organometallics that give signal at negative.
In samples where natural hydrogen h is used practically all the hydrogen consists of the isotope 1 h hydrogen 1.
A the chemical shifts of these protons vary in different solvents and with temperature and concentration table of carbon 13 chemical shifts.
In fact the 1 h nmr spectra of most organic molecules contain proton signals that are split into two or more sub peaks.
We know that a proton alpha to a carbonyl group is pulled downfield.
Vinylic r 2 c crh.
Alternative sites exist that have an introduction to nmr theory.
This is a standard reference point with the signal set exactly at 0 ppm and you can ignore it when analyzing an nmr spectrum.
The source of spin spin coupling.
0 at the vinylic protons.
Table showing proton chemical shifts.
1 h nmr chemical shifts.
Consequently their nmr absorptions occur at relatively high chemical shift.
Chemical shift d type of proton examples chemical shift in ppm comments.
Table of characteristic proton nmr shifts type of proton type of compound chemical shift range ppm rch 3 1 aliphatic 0 9 r 2 ch 2 2 aliphatic 1 3 r 3 ch 3 aliphatic 1 5 c c h vinylic 4 6 5 9 c c h vinylic conjugated 5 5 7 5 c c h acetylenic 2 3 ar h aromatic 6 8 5 ar c h benzylic 2 2 3 c c ch 3 allylic 1 7 hc f.
In other words frequencies for chemicals are measured for a 1 h or 13 c nucleus of a sample from the 1 h or 13 c resonance of tms.
As a result the vinylic protons are subjected to a greater local field.
This is a general trend add approximately 0 2 0 4 ppm for each additional alkyl group.
The greater the substitution on the carbon bearing the hydrogen the further downfield higher frequency the resonance occurs.
The source of spin spin coupling.
The only peak that comes before saturated c h protons is the signal of the protons of tetramethylsilane ch3 4 si also called tms.
This is not surprising since the proton is not only vinylic but it is also alpha to a carbonyl group.